What Is a JavaServer Faces Application?
The functionality provided by a JavaServer Faces application is similar to that of any other Java web application. A typical JavaServer Faces application includes the following parts.
-
A set of web pages in which components are laid out.
-
A set of tags to add components to the web page.
-
A set of managed beans, which are lightweight, container-managed objects (POJOs). In a JavaServer Faces application, managed beans serve as backing beans, which define properties and functions for UI components on a page.
-
A web deployment descriptor (
web.xmlfile). -
Optionally, one or more application configuration resource files, such as a
faces-config.xmlfile, which can be used to define page navigation rules and configure beans and other custom objects, such as custom components. -
Optionally, a set of custom objects, which can include custom components, validators, converters, or listeners, created by the application developer.
-
Optionally, a set of custom tags for representing custom objects on the page.
Figure 7-1 shows the interaction between client and server in a typical JavaServer Faces application. In response to a client request, a web page is rendered by the web container that implements JavaServer Faces technology.
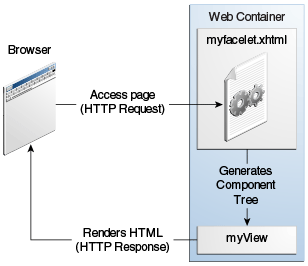
The web page, myfacelet.xhtml, is built using JavaServer Faces
component tags. Component tags are used to add components to the view
(represented by myView in the diagram), which is the server-side
representation of the page. In addition to components, the web page can
also reference objects, such as the following:
-
Any event listeners, validators, and converters that are registered on the components
-
The JavaBeans components that capture the data and process the application-specific functionality of the components
On request from the client, the view is rendered as a response. Rendering is the process whereby, based on the server-side view, the web container generates output, such as HTML or XHTML, that can be read by the client, such as a browser.
