Packaging Web Archives
In the Java EE architecture, a web module is the smallest deployable and usable unit of web resources. A web module contains web components and static web content files, such as images, which are called web resources. A Java EE web module corresponds to a web application as defined in the Java Servlet specification.
In addition to web components and web resources, a web module can contain other files:
-
Server-side utility classes, such as shopping carts
-
Client-side classes, such as utility classes
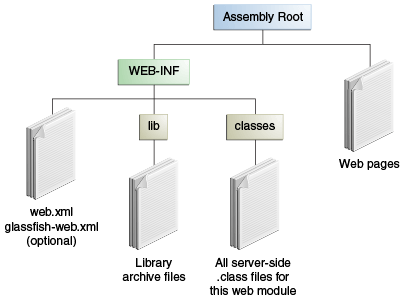
A web module has a specific structure. The top-level directory of a web module is the document root of the application. The document root is where XHTML pages, client-side classes and archives, and static web resources, such as images, are stored.
The document root contains a subdirectory named WEB-INF, which can
contain the following files and directories:
-
classes, a directory that contains server-side classes: servlets, enterprise bean class files, utility classes, and JavaBeans components -
lib, a directory that contains JAR files that contain enterprise beans, and JAR archives of libraries called by server-side classes -
Deployment descriptors, such as
web.xml(the web application deployment descriptor) andejb-jar.xml(an EJB deployment descriptor)
A web module needs a web.xml file if it uses JavaServer Faces
technology, if it must specify certain kinds of security information, or
if you want to override information specified by web component
annotations.
You can also create application-specific subdirectories (that is,
package directories) in either the document root or the
WEB-INF/classes/ directory.
A web module can be deployed as an unpacked file structure or can be
packaged in a JAR file known as a Web Archive (WAR) file. Because the
contents and use of WAR files differ from those of JAR files, WAR file
names use a .war extension. The web module just described is portable;
you can deploy it into any web container that conforms to the Java
Servlet specification.
You can provide a runtime deployment descriptor (DD) when you deploy a
WAR on GlassFish Server, but it is not required under most
circumstances. The runtime DD is an XML file that may contain such
information as the context root of the web application, the mapping of
the portable names of an application’s resources to GlassFish Server
resources, and the mapping of an application’s security roles to users,
groups, and principals defined in GlassFish Server. The GlassFish Server
web application runtime DD, if used, is named glassfish-web.xml and is
located in the WEB-INF directory. The structure of a web module that
can be deployed on GlassFish Server is shown in Figure
5-3.