Table of Contents
- 10.1. Introduction to Reliable Messaging
- 10.2. Configuring Web Service Endpoint
- 10.3. Configuring Web Service Client
- 10.4. Configurable features summary
- 10.5. Creating Web Service Providers and Clients that use Reliable Messaging
- 10.6. Using Secure Conversation With Reliable Messaging
- 10.7. High Availability Support in Reliable Messaging
In the SOAP messaging world, presence of software, system or network failures is a common issue web service developers need to deal with. This issue is even more obvious in mobile applications which access the corporate network through mobile-enabled channels with limited connectivity and connection quality, such as WiFi, UMTS or GPRS.
WS-ReliableMessaging specification, an OASIS standard, addresses this issue by defining a modular mechanism for reliable transfer of messages. It defines a messaging protocol to identify, track, and manage the reliable transfer of messages between a source and a destination in an interoperable fashion. The modularity and the extension points defined in the mechanism allows integration of other quality of service features, such as message level security.
Metro implementation of reliable messaging is based o WS-ReliableMessaging. As other Quality of Service features, Reliable Messaging is configured via WS-Policy expressions stored in the WSDL document of a web service or in the web service's WSIT configuration file. These XML-based expressions are designed for machine processing rather than for human readability. Metro comes with a tooling support in the form of a plug-in for NetBeans IDE which provides a convenient way to configure reliable messaging feature for your web services. It provides a dialog-based wizard that lets you fine-tune a few reliable messaging configuration properties. In general, the properties you configure on the web service endpoint apply to the web service client as well. On the other hand, the client-side configuration options have only local effect and let you tweak the client-specific behavior.
In the following sections we will look at enabling reliable messaging with Metro in more detail. These sections also contain tables that describe configuration options in more detail for service endpoint (Configuring Web Service Endpoint) as well as service client (Reliable Messaging Configuration Options for Service Client) side.
When creating a reliable web service, you first start by creating a web service using common steps described in section Developing with NetBeans. Once the web service is created, a design view of the web service should open in the editor window. If the design view is not opened, locate your web service in the Projects view and double-click the web service to open it in the editor window.
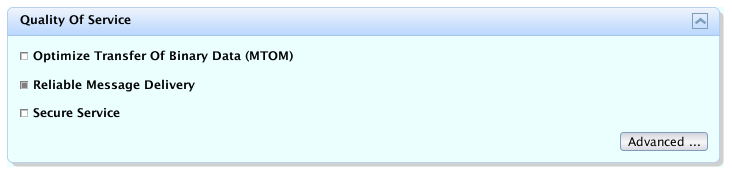
In the design view, there is a Quality of Service section as show on the picture below:
In this section you may either simply check the
Reliable Message Delivery checkbox and accept the
Reliable Messaging configuration defaults, which means that your RM
configuration for your web service is done, or you may click the
button to display the
Quality of Service dialog as shown on the picture
below.
Note
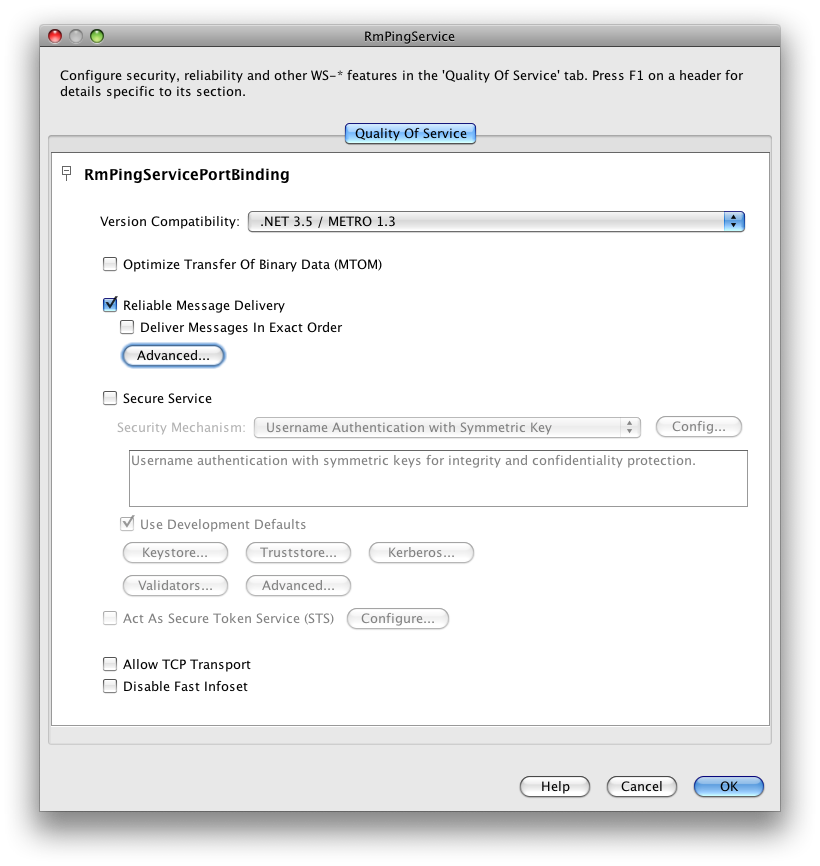
You may alternatively access the Quality of Service dialog by right clicking on a web service in the Projects view and selecting Edit Web Service Attributes from the context pop-up menu.
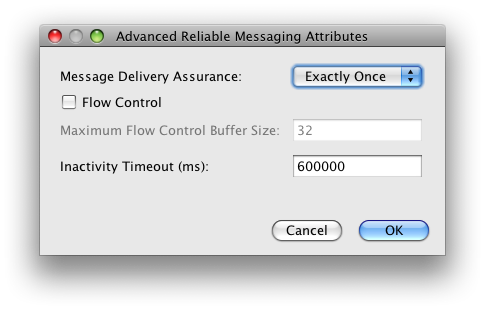
The Quality of Service dialog contains more configuration options for Reliable Messaging. Some of these are accessible direclty while the most advance configuration details are hidden behind the Advanced button in a seprate dialog presented on the next picture.
In order to provide better overview of the RM configuration options, we included the following table that povides a detailed description of all the reliable messaging configuration options available on the service endpoint.
Table 10.1. Reliable Messaging Configuration Options for Service Endpoint
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Reliable Message Delivery | Enables or disables reliable messaging feature. |
| Deliver Messages In Exact Order | Specifies whether the Reliable Messaging protocol ensures that the application messages for a given message sequence are delivered to the endpoint application in the order indicated by the message numbers. This option increases the time to process application message sequences and may result in the degradation of web service performance. Therefore, you should not enable this option unless ordered delivery is required by the web service. |
| Message Delivery Assurance | This option tells our Reliable Messaging
implementation what type of the message delivery
assurance is expected. Currently it can be set to
"Exactly Once" and "At Least Once".
|
| Flow Control | Enables or disables the flow control feature. When enabled, this feature works in conjunction with the Max Buffer Size setting to determine the maximum number of messages for sequence that can be stored at the endpoint awaiting delivery to the application. Messages may have to be withheld from the application if ordered delivery is required and some of their predecessors have not arrived. If the number of stored messages reaches the threshold specified in the Max Buffer Size setting, incoming messages belonging to the sequence are ignored. |
| Maximum Flow Control Buffer Size | If Flow control is enabled, this value specifies the number of request messages that will be buffered in the RM session. The default setting is 32. For more information, see the description of the Flow Control option. |
| Inactivity Timeout | Specifies the time interval beyond which either source or destination may terminate the RM session due to inactivity. The default setting is 600,000 milliseconds (10 minutes). A web service endpoint will always terminate session whose inactivity timeout has expired. This option may be used to ensure the early removal of stale RM sequences and thus reduce the memory footprint of the service endpoint. Note that setting the value of this option affects also the web service proxy usage patterns in the client applications. |
While most of the Reliable Messaging options are configured on the web service endpoint, there are some details that may be fine-tuned on the client side as well. To configure the client-side details of Reliable Messaging you first need to create a web service proxy. Section Creating a Client to Consume a WSIT-Enabled Web Service describes all the necessary steps.
Once a web service proxy is created, you can find it in the Projects view under Web Service References item. By right-clicking on the we service proxy and selecting Edit Web Service Attributes from the opened context pop-up menu you may open a dialog that let's you specify additional RM details.
When dialog opens, it may have multiple tabs. The Reliable messaging configuration options are located on the Quality of Service tab in Advanced Configuration section. Following table describes all the reliable messaging configuration options available on the web service client side.
Table 10.2. Reliable Messaging Configuration Options for Service Client
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| RM Resend Interval | The time in milliseconds after which the sender (RMSource) attempts to redeliver unacknowledged messages to the Reliable Messaging Destination (RM-enabled WS endpoint). By default, resend happen every 2000ms. |
| RM Close Timeout | By default, the call to proxy.close() will not return until all messages have been acknowledged. RM close timeout is the interval (in milliseconds) that the client runtime will block waiting for a call to close() to return. If there are still unacknowledged messages after this interval is reached, and the call to close has returned, an error will be logged about messages being lost. |
| RM Ack Request Interval | The suggested minimum time that the sender (RMSource) should allow to elapse between sending consecutive Acknowledgement request messages to the Reliable Messaging Destination (RM-enabled WS endpoint). |
In the previous chapter we focused on configuring Metro reliable messaging using NetBeans IDE. This section is a summary of all Metro reliable messaging runtime features that can be configured since Metro v2.0 and higher. The summary lists all the features discussed before as well as all other features that can be only configured by manually editing the WSIT config file.
Please note that this chapter focuses on features configurable with Metro v2.0 and higher.
Table 10.3. Namespaces used within Metro Reliable Messaging WS-Policy Assertions
| Prefix | Namespace |
|---|---|
| wsp | http://www.w3.org/ns/ws-policy |
| wsrmp10 | http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/02/rm/policy |
| wsrmp | http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-rx/wsrmp/200702 |
| net30rmp | http://schemas.microsoft.com/net/2005/02/rm/policy |
| net35rmp | http://schemas.microsoft.com/ws-rx/wsrmp/200702 |
| sunrmp | http://sun.com/2006/03/rm |
| sunrmcp | http://sun.com/2006/03/rm/client |
| metro | http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/metro/ws-rx/wsrmp/200702 |
Table 10.4. Reliable Messaging Configuration Features - Layout
| Feature name |
| Description |
| WS-RM 1.0 compatible assertion |
| WS-RM 1.1+ compatible assertion |
Table 10.5. Enable Reliable Messaging + version
| Enable Reliable Messaging + version |
| Specifies that WS-ReliableMessaging protocol MUST be used when sending messages. Defines also the version of the WS-RM protocol to be used. |
/wsrmp10:RMAssertion |
/wsrmp:RMAssertion |
Table 10.6. Sequence Inactivity Timeout
| Sequence Inactivity Timeout |
| Specifies the time interval beyond which either RM Source or RM Destination may terminate the RM sequence due to inactivity. The default setting is 600,000 milliseconds (10 minutes). A web service endpoint will always terminate session whose inactivity timeout has expired. Specified in milliseconds. |
/wsrmp10:RMAssertion/wsrmp10:InactivityTimeout |
/net35rmp:InactivityTimeout |
Table 10.7. Acknowledgement interval
| Acknowledgement interval |
| Specifies the duration after which the RM Destination will transmit an acknowledgement. If omitted, there is no implied value. Specified in milliseconds. |
/wsrmp10:RMAssertion/wsrmp10:AcknowledgementInterval |
/net35rmp:AcknowledgementInterval |
Table 10.8. Retransmission Interval
| Retransmission Interval |
| Specifies how long the RM Source will wait after transmitting a message and before retransmitting the message. If omitted, there is no implied value. Specified in milliseconds. |
/wsrmp10:RMAssertion/wsrmp10:BaseRetransmissionInterval/sunrmcp:ResendInterval |
/metro:RetransmissionConfig/metro:Interval |
Table 10.9. Retransmission Interval Adjustment Algorithm
| Retransmission Interval Adjustment Algorithm |
| Specifies that the retransmission interval will be adjusted using a specific (e.g. exponential back-off) algorithm. |
("Exponential backoff" algorithm only) |
/metro:RetransmissionConfig/metro:Algorithm |
Table 10.10. Maximum Retransmission Count
| Maximum Retransmission Count |
A message is considered to be transferred if its delivery at the recipient has been acknowledged by the recipient. If an acknowledgment has not been received within a certain amount of time for a message that has been transmitted, the infrastructure automatically retransmits the message. The infrastructure tries to send the message for at most a preconfigured number of times. Not receiving an acknowledgment before this limit is reached is considered a fatal communication failure, and causes the RM session to fail. |
| N/A |
/metro:RetransmissionConfig/metro:MaxRetries |
Table 10.11. Close sequence timeout
| Close sequence timeout |
| By default, the call to proxy.close() will not return until all messages have been acknowledged. RM close timeout is the interval (in milliseconds) that the client runtime will block waiting for a call to close() to return. If there are still unacknowledged messages after this interval is reached, and the call to close has returned, an error will be logged about messages being lost. |
(client side only) |
/metro:CloseSequenceTimeout |
Table 10.12. Acknowledgement request interval
| Acknowledgement request interval |
| Defines the suggested minimum time that the sender (RM Source) should allow to elapse between sending consecutive Acknowledgement request messages to the RM Destination. |
/sunrmcp:AckRequestInterval |
/metro:AckRequestInterval |
Table 10.13. Bind RM sequence to security token
| Bind RM sequence to security token |
| Defines the requirement that an RM Sequence MUST be bound to an explicit token that is referenced from a wsse:SecurityTokenReference in the CreateSequence message. |
| N/A |
/wsrmp:RMAssertion/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:SequenceSTR |
Table 10.14. Bind RM sequence to secured transport
| Bind RM sequence to secured transport |
| Defines the requirement that an RM Sequence MUST be bound to the session(s) of the underlying transport-level protocol used to carry the CreateSequence and CreateSequenceResponse message. (When present, this assertion MUST be used in conjunction with the sp:TransportBinding assertion.) |
| N/A |
/wsrmp:RMAssertion/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:SequenceTransportSecurity |
Table 10.15. Exactly once delivery
| Exactly once delivery |
| Each message is to be delivered exactly once; if a message cannot be delivered then an error MUST be raised by the RM Source and/or RM Destination. The requirement on an RM Source is that it SHOULD retry transmission of every message sent by the Application Source until it receives an acknowledgement from the RM Destination. The requirement on the RM Destination is that it SHOULD retry the transfer to the Application Destination of any message that it accepts from the RM Source until that message has been successfully delivered, and that it MUST NOT deliver a duplicate of a message that has already been delivered. |
| default |
/wsrmp:RMAssertion/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:DeliveryAssurance/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:ExactlyOnce |
Table 10.16. At Most once delivery
| At Most once delivery |
| Each message is to be delivered at most once. The RM Source MAY retry transmission of unacknowledged messages, but is NOT REQUIRED to do so. The requirement on the RM Destination is that it MUST filter out duplicate messages, i.e. that it MUST NOT deliver a duplicate of a message that has already been delivered. |
| N/A |
/wsrmp:RMAssertion/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:DeliveryAssurance/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:AtMostOnce |
Table 10.17. At Least once delivery
| At Least once delivery |
| Each message is to be delivered at least once, or else an error MUST be raised by the RM Source and/or RM Destination. The requirement on an RM Source is that it SHOULD retry transmission of every message sent by the Application Source until it receives an acknowledgement from the RM Destination. The requirement on the RM Destination is that it SHOULD retry the transfer to the Application Destination of any message that it accepts from the RM Source, until that message has been successfully delivered. There is no requirement for the RM Destination to apply duplicate message filtering. |
/sunrmcp:AllowDuplicates |
/wsrmp:RMAssertion/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:DeliveryAssurance/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:AtLeastOnce |
Table 10.18. InOrder delivery
| InOrder delivery |
| Messages from each individual Sequence are to be delivered in the same order they have been sent by the Application Source. The requirement on an RM Source is that it MUST ensure that the ordinal position of each message in the Sequence (as indicated by a message Sequence number) is consistent with the order in which the messages have been sent from the Application Source. The requirement on the RM Destination is that it MUST deliver received messages for each Sequence in the order indicated by the message numbering. This DeliveryAssurance can be used in combination with any of the AtLeastOnce, AtMostOnce or ExactlyOnce assertions, and the requirements of those assertions MUST also be met. In particular if the AtLeastOnce or ExactlyOnce assertion applies and the RM Destination detects a gap in the Sequence then the RM Destination MUST NOT deliver any subsequent messages from that Sequence until the missing messages are received or until the Sequence is closed. |
/sunrmp:Ordered |
/wsrmp:RMAssertion/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:DeliveryAssurance/wsp:Policy/wsrmp:InOrder |
Table 10.19. Flow Control
| Flow Control |
| Enables or disables the flow control feature. When enabled, this feature works in conjunction with the Max Buffer Size setting to determine the maximum number of messages for sequence that can be stored at the endpoint awaiting delivery to the application. Messages may have to be withheld from the application if ordered delivery is required and some of their predecessors have not arrived. If the number of stored messages reaches the threshold specified in the Max Buffer Size setting, incoming messages belonging to the sequence are ignored. |
/net30rmp:RmFlowControl |
/net30rmp:RmFlowControl |
Table 10.20. Maximum Flow Control Buffer Size
| Maximum Flow Control Buffer Size |
| If Flow control is enabled, this value specifies the number of request messages that will be buffered in the RM session. The default setting is 32. For more information, see the description of the Flow Control option. |
/net30rmp:RmFlowControl/net30rmp:MaxReceiveBufferSize |
/net30rmp:RmFlowControl/net30rmp:MaxReceiveBufferSize |
Table 10.21. Maximum concurrent RM sessions
| Maximum concurrent RM sessions |
| Specifies how many concurrently active RM sessions (measured based on inbound RM sequences) the SequenceManager dedicated to the WS Endpoint accepts before starting to refuse new requests for sequence creation. |
| N/A |
/metro:MaxConcurrentSessions |
Table 10.22. Reliable Messaging Persistence
| Reliable Messaging Persistence |
| Specifies whether the runtime should use persistent sequence and message storage or not. |
| N/A |
/metro:Persistent |
Table 10.23. Sequence manager maintenace task execution period
| Sequence manager maintenace task execution period |
| Specifies the period (in milliseconds) of a sequence maintenance task execution. Sequence maintenance task takes care of terminating inactive sequences and removing the terminated sequences from the sequence repository. |
| N/A |
/metro:MaintenanceTaskPeriod |
Examples and detailed instructions on how to create web service providers and clients that use reliable messaging are provided in the following chapters:
For an example of creating a web service and a client using a web container and NetBeans IDE, see Developing with NetBeans.
For an example of creating a web service and a client using only a web container, see WSIT Example Using a Web Container Without NetBeans IDE.
If Secure Conversation is enabled for the web service endpoint, the web service acquires a Security Context Token (SCT) for each application message sequence, that is, each message sequence is assigned a different SCT. The web service then uses that token to sign all messages exchanged for that message sequence between the source and destination for the life of the sequence. Hence, there are two benefits in using Secure Conversation with Reliable Messaging:
The sequence messages are secure while in transit between the source and destination endpoints.
If there are different users accessing data at the source and destination endpoints, the SCT prevents users from seeing someone else's data.
Note
Secure Conversation is a WS-Security option, not a reliable messaging option. If Secure Conversation is enabled on the web service endpoint, Reliable Messaging uses Security Context Tokens.
For more information on how to use Secure Conversation, see Using WSIT Security.
Starting with the Metro 2.1 release Metro implementation of reliable messaging supports deployment in clustered environment configurations of the GlassFish Application Server 3.1 and higher. The only untested and thus currently officially unsupported reliable messaging feature in an HA environment is in-order message delivery. For more details see RM section of the WSIT 2.1 Release Notes.
For a general overview of Metro High Availability support, please consult High Availability Support in Metro section.